Research
Current Projects
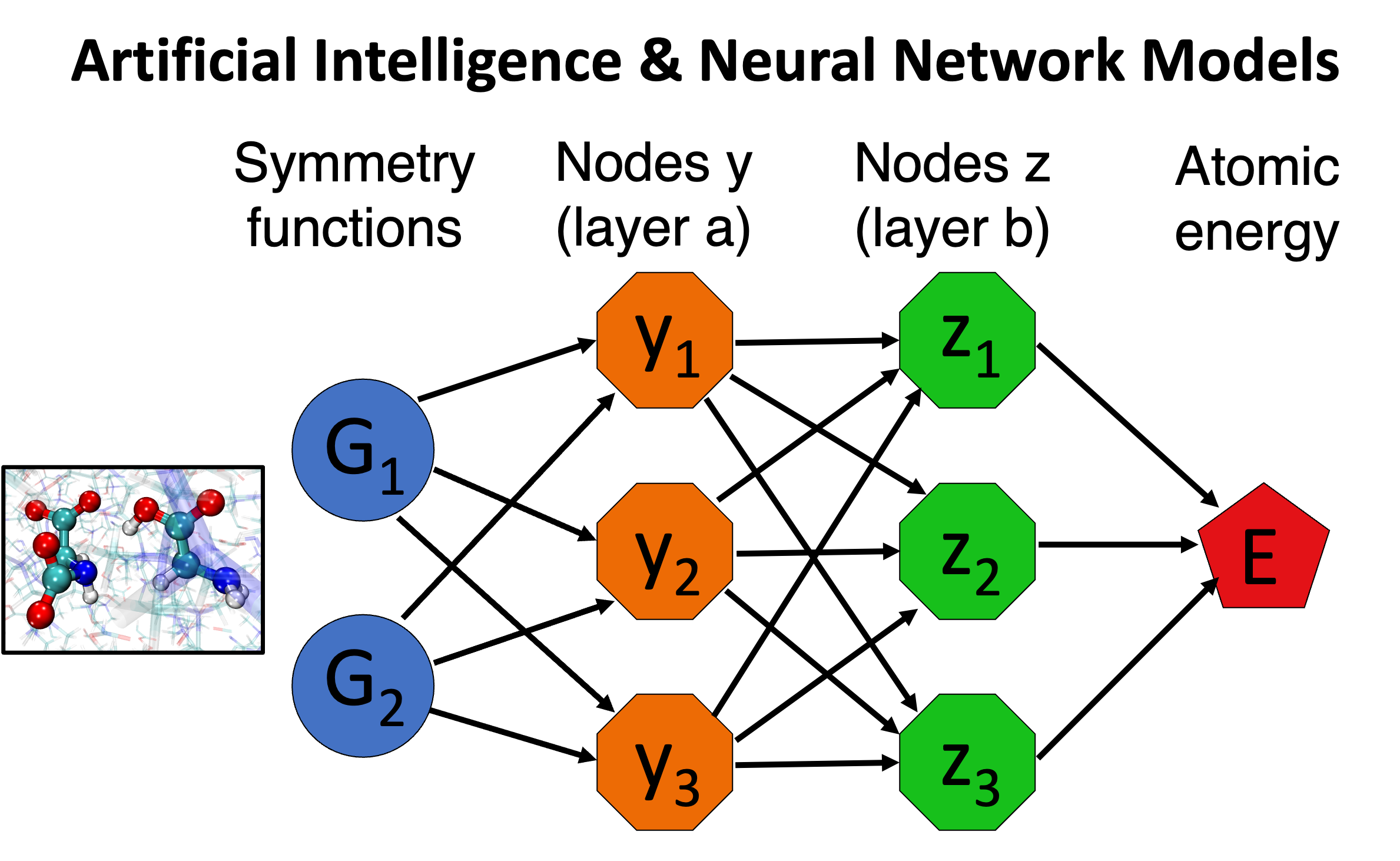
Harnessing and implementing artificial intelligence (AI) and neural network models for complex physicochemical processes are essential for achieving more realistic and efficient simulations, especially for green growth and sustainability. These models, while preserving important physical principles, enable accurate predictions of material behavior over extended spatial and temporal scales—something traditional methods often struggle to achieve. By utilizing AI, we can accelerate the discovery and optimization of green materials and environmentally sustainable processes, thereby addressing complex challenges in chemistry, materials science, and engineering. Ultimately, this approach enhances our ability to conduct scalable and accurate simulations, bringing theoretical insights closer to real-world applications pertinent to sustainable technologies.
The Yoon Group develops advanced computational and data-driven strategies to accelerate discovery across chemical catalysis, biocatalysis, and electrocatalysis. We integrate artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and multiscale modeling to understand and design catalytic systems spanning molecular, interfacial, and condensed-phase environments. By bridging quantum mechanical simulations, molecular dynamics, and continuum-scale modeling, we uncover fundamental reaction mechanisms, energy landscapes, and dynamic solvent or interfacial effects that govern catalytic performance. Our approach enables predictive design of metal and heterogeneous catalysts, enzyme-mediated transformations, and electrochemical interfaces relevant to sustainable chemical manufacturing, carbon conversion, and energy technologies. Through the synergy of physics-based modeling and data-driven learning, we aim to transform how catalytic materials and processes are discovered and optimized.
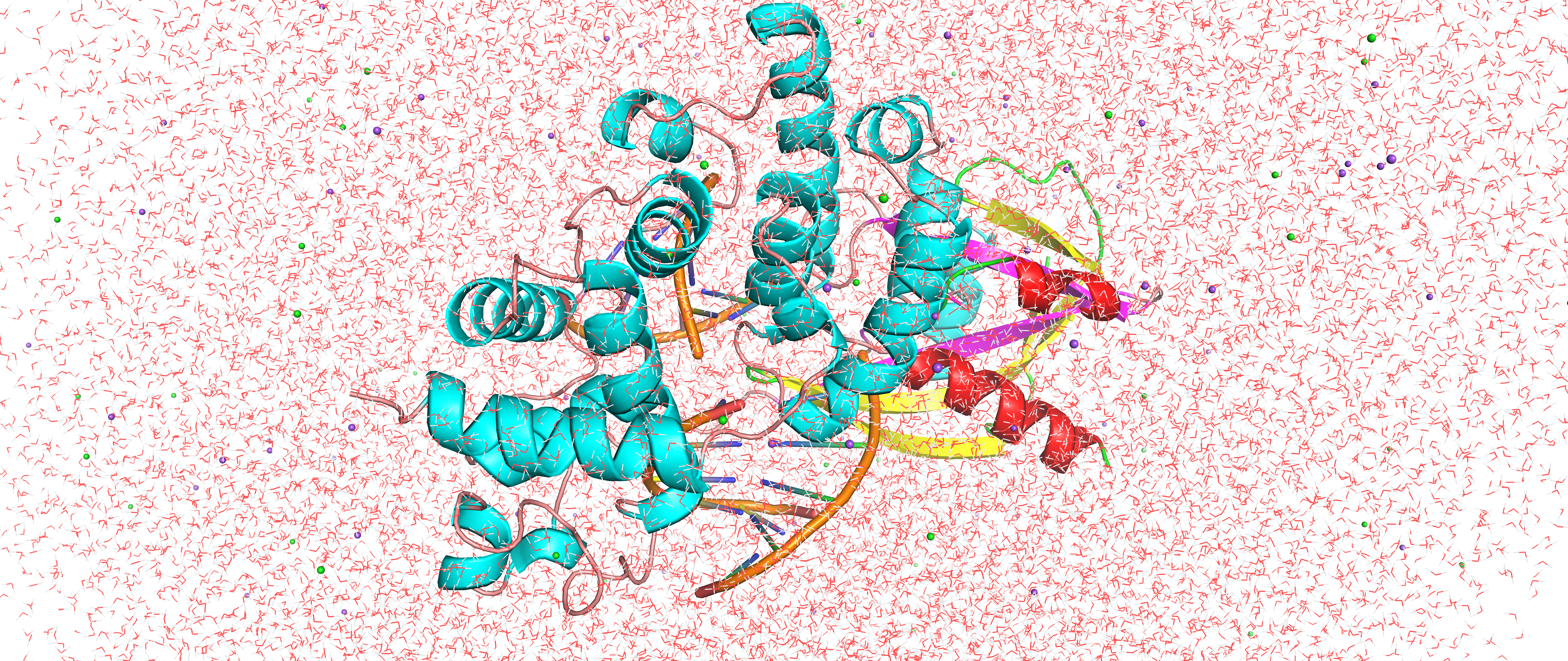
Studying biomolecular modeling is crucial because it allows us to understand the intricate mechanisms of enzymatic reactions at a molecular level, which are essential for life processes. Through multiscale computational simulations, we can investigate and visualize how enzymes interact with substrates, predict reaction pathways, and identify key factors influencing enzyme efficiency and specificity. This understanding aids in the design of novel drugs and therapeutic interventions by targeting specific enzymes linked to diseases. Additionally, it provides insights into enzyme evolution and aids in the development of biocatalysts for more sustainable chemical processes.

Our group leverages cutting-edge multiscale simulations and physics-based machine learning to investigate the molecular mechanisms of biomass conversion into value-added chemicals and fuels. By modeling thermodynamic and kinetic processes at the atomic and molecular level, we aim to unravel reaction pathways and optimize catalyst-solvent environments for efficient, sustainable transformation of lignocellulosic, aquatic, and waste-derived biomasses. These computational insights guide the rational design of green processing strategies, supporting innovations in carbon-neutral chemical processes. Through theory- and computation-driven discovery, we contribute to the broader goal of sustainable energy and the advancement of green chemistry.
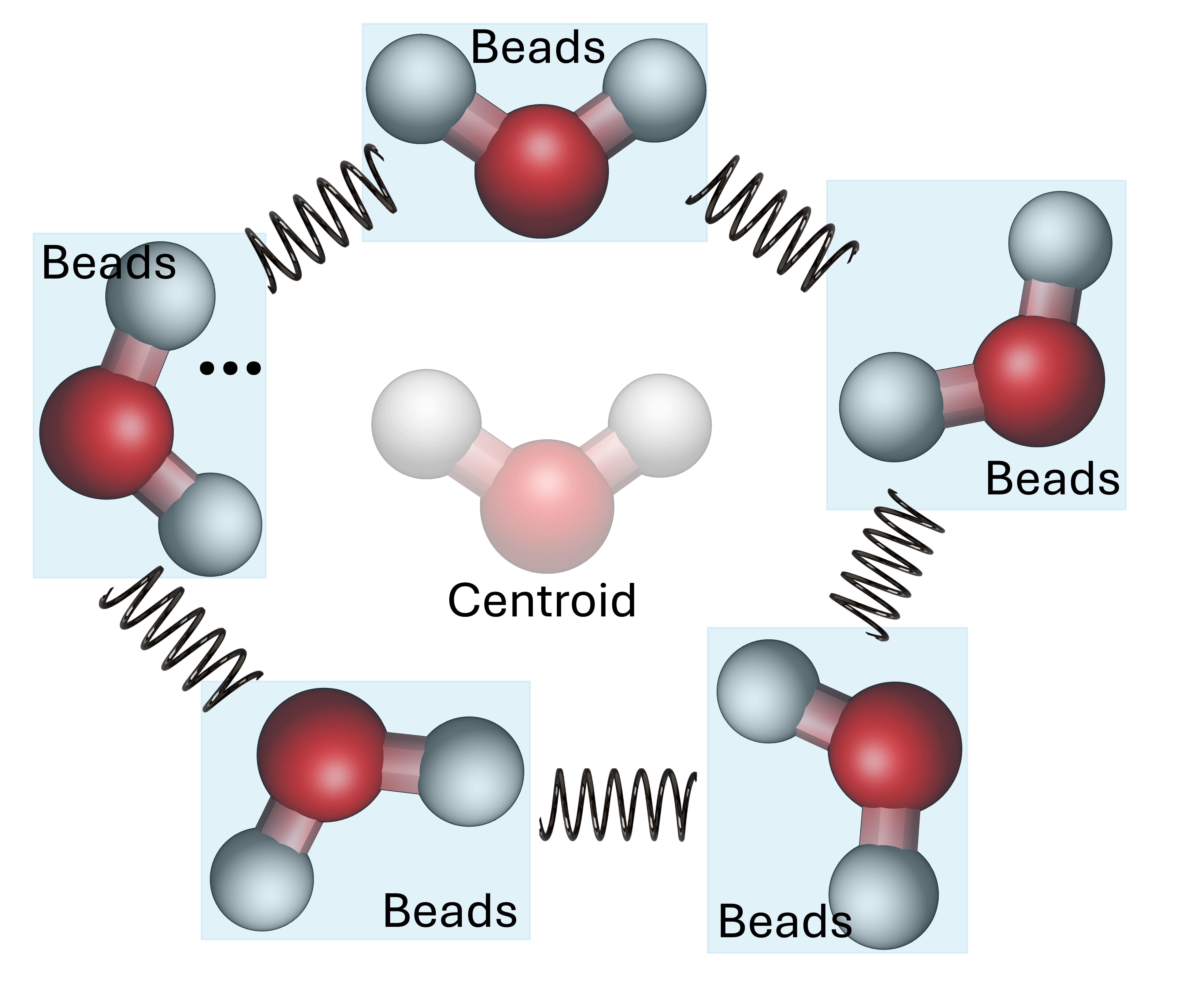
Our group employs advanced molecular dynamics techniques to capture essential quantum effects, such as zero-point energy (ZPE) retention, quantum tunneling, and nuclear delocalization, which are critical for understanding chemical reactivity, catalysis, and condensed-phase molecular systems. We leverage quantum-enhanced simulation methods to compute reaction rates, dynamical properties, and quantum-corrected correlation functions, enabling accurate descriptions of transport and thermodynamic behavior. These approaches allow us to investigate isotope effects, proton and hydrogen transfer, phase transitions, and nuclear quantum effects in materials, aqueous, and condensed phase systems, which are not accessible through classical simulations. By systematically incorporating nuclear quantum effects, our research provides a more accurate molecular-level understanding of reaction mechanisms, charge transport, and structural dynamics in complex environments. Our work bridges the gap between classical and quantum models, offering deeper insights into fundamental processes that govern sustainable energy systems, catalysis, and environmental chemistry and engineering.
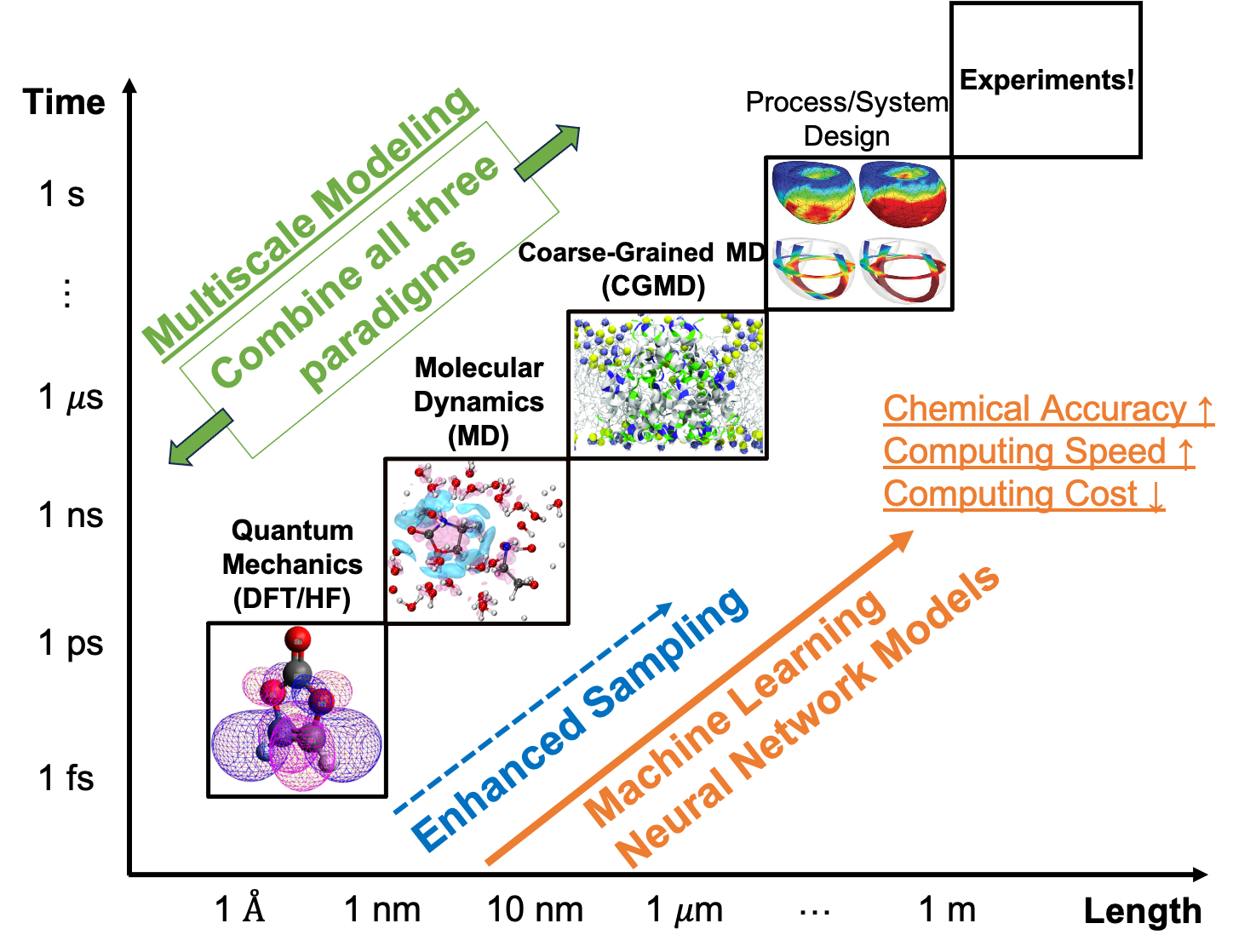
Developing and applying multiscale simulations, from quantum mechanics to coarse-grained molecular dynamics and continuum scale modeling, is essential for addressing energy and sustainability challenges. These simulations enable us to understand and optimize complex processes across different scales, from atomic-level reactions to large-scale system behavior, which is critical for designing efficient energy conversion and storage systems. By integrating and connecting insights from various scales with enhanced sampling methods, we can develop more sustainable materials and technologies that minimize environmental impact, such as advanced biological and catalytic processes. Additionally, this approach helps in predicting the performance and lifetime of energy-related materials and systems under realistic operating conditions, guiding the development of future sustainable solutions.